HEART ARTICLES
ARTICLE 1
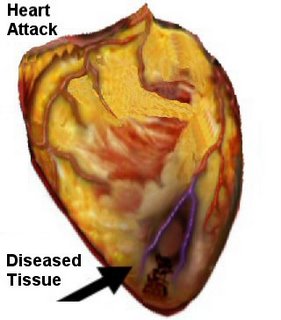
Heart Attack
In This Article
· Common Names For a heart attack
· What is A heart Attack
· Warning signs of A heart attack
· Who is at risk from a heart attack
Common Names For a heart attack
A heart attack goes under many names including the following: -
· Myocardial infarction or MI,
· Acute myocardial infarction or AMI
· Acute coronary syndrome
· Coronary thrombosis
· Coronary occlusion
What is A heart Attack
A myocardial infarction occurs when an area of the heart’s muscle dies or is permanently damaged because of inadequate supply of oxygen, which results from a blockage.
The blockage is usually caused in the coronary artery as the blockage results in a arrhythmia, which is an irregular heart rhythm. This irregular heartbeat may prevent the pumping function of the heart and as this is the primary heart function it can lead to death. If death does not occur immediately the blockage must be treated with a few hours or the area of the heart muscle, which has been affected by the arrhythmia, will die and be replaced by scar tissue.
A clot in the coronary artery interrupts the flow of blood and oxygen to the heart muscle, leading to the death of heart cells in the immediate vicinity. The damaged heart muscle loses its ability to contract, and the remaining heart muscle needs to compensate for that weakened area. The larger the area of the heart that is damaged means that the remaining “healthy” area cannot cope. This is critical because of the blood supply ceases for more than a few minutes permanent damage is caused in the muscle cells, which results in death or permanent disablement. Statistically a million people in the U.S. suffer a heart attack annually and fifty percent die, of these deaths just over a half will die in the first hour following the heart attack.
The brutal truth of a heart attack is that emergency treatment must be sought IMMEDIATELY you suspect that a heart attack is occurring. Emergency procedures can be implemented to restore the flow of blood to the blocked artery, and this can prevent permanent damage to the heart. Statistically most people do not seek treatment until over two hours after the start of symptoms, and many leave it for over twelve hours. Prompt action saves lives in this situation, as the delay is unsustainable in many cases.
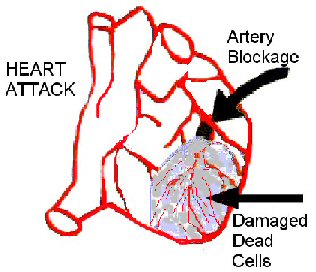
The clot has usually formed in the coronary artery as a r4esult of narrowing due to atherosclerosis. The atherosclerotic plaque inside the arterial wall sometimes cracks or splinters, which trigger the formation of a clot, which may be called a thrombus, leading to the adjective thrombosis.
Warning signs of A heart attack
The warning signs are approximate because the symptoms of a heart attack are too diverse to be simplified. As can be seen these signs are very easily confused with non life threatening inconsequential conditions such as eating too much! However the damage and death resulting from a heart attack are serious enough not to be trivialized or ignored, and the survivor’s of a heart attack are those that took the decision to be safe not sorry. The sooner treatment is administered the safer a patient will be.
Who Is at Risk From A Heart Attack?
There is no such thing as a typical profile for a heart attack victim, but it is certain that it is the number one killer in the most of the first world today. There are some risk factors that are irrefutable –
· Advancing age
Over 80 percent of people who die of coronary heart disease are 65 years of age or older.
Beyond this age women are more likely to die than men when they have a heart attack, although it may not be immediate it may be within a few weeks.
· Gender
After menopause women have a higher risk than men of not surviving a heart attack, but men have heart attacks earlier and more often.
· Heredity Factors
Statistically Africans have a higher rate of blood pressure than Caucasians and their risk of having a heart attack is proportionally higher. Some Asian groups have higher risk Gujarati’s tend to have a higher number of heart attacks, as do Mexicans and Polynesians. However the factors are not necessarily genetic they may be as a result of higher obesity rate coupled with higher levels of the onset of middle age diabetes.
In comclusion, there are some riskl factors that there is little you can do about, but that fact alone makes it more crucial that the things you can do such as keeping your weight within a safe band, have regular exercise and look at your levels of cholesterol and blood pressure.
ARTICLE 2
Heart Attack Symptoms
In This Article
· Variations in Symptoms.
· Coronary Heart Disease
· General Indicators Of a Heart Attack
· Angina as a precursor of a heart attack.
· Silent Heart Attacks
Variations in Symptoms.
The bad news for a assessing whether or not you are suffering from a heart attack is that no single heart attack resembles any other, and even if you have had one before there is no guarantee that the symptoms will be the same. The symptoms of a heart attack depends on the severity of a heart attack and how much damage is caused to the heart cells, whether they actually die or are damaged. To further complicate matter there are silent heart attacks that occur without any symptoms.
General Indicators Of a Heart Attack
· Chest discomfort.
The majority of heart attacks involve discomfort in the chest that either lasts for more than a few minutes, or goes away and returns. This discomfort can take many forms it is not always pain, it may be pressure a feeling of fullness, contracting or squeezing of the chest. Also it may be confused with minor ailments such as heartburn or indigestion because it may indeed manifest the first symptoms.
· Discomfort in other areas of the upper body.
There may be pain, discomfort, or a sense of numbness in one or both of the arms, the back, neck, jaw, or the stomach.
· Shortness of breath.
May or may not accompany a heart attack, it may come before during or after the heart attack itself.
· Other symptoms.
These may be cold sweats, leaving a film of sweat on the skin or a feeling of clamminess. The patient may feel light headed or dizzy, as if they have sat up too quickly, or they may feel nausea and want to vomit.
· Gender symptoms
Women statistically have a greater risk of experiencing pain between the shoulders and this tends to make then defer diagnosis and therefore treatment.
· Coronary Heart Disease or angina.
The heart like any other of the human body organs needs sufficient oxygen to function, and if deprived of this it will react and cause pain. The correct name for this condition is
Myocardial ischemia.
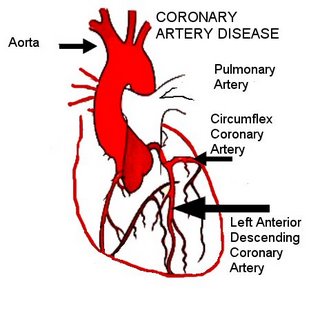
· Angina as A Precursor of a Heart Attack.
Typically the heart tends to beat faster after a big meal, during and after hard physical exertion, in the cold, or during periods of stress or emotional discomfort. If the arteries cannot supply enough oxygen in these charged times then the heart suffers from oxygen deficiency and it reacts by creating pain known as angina pectoris.
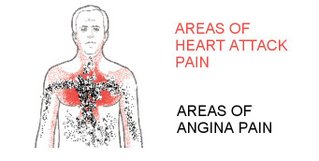
Whilst it is difficult to tell if a pain is indeed a heart attack pain, the pain resulting from angina pectoris tends to be distinct and is often described as a strangulating pain or a feeling of suffocation. It tends to be more severe and intense than heartburn or indigestion In may cases it appears to start under the breastbone and radiates on the left side to the throat, neck, shoulder and maybe as far down as the arm, it can in rarer cases emanate on the right side as well.
As a result of its intensity the first angina attack can be frightening, but despite the severity of the pain, they generally subside after about fifteen twenty minutes. In the event of them lasting longer a medical check up should be sought immediately. If angina carries on for a long time it may well lead to a full blown heart attack.
· Silent Heart Attacks
These can occur with no symptoms and therefore no treatment will be sought, but statistically they are more likely to happen to women, diabetics and those over 65.
ARTICLE 3
How TO Prevent Heart Attacks.
In this Article
· Heart Attack
· Risk factors for a heart attack
· Assessing Individual risk of a heart attack
Heart Attack
A heart attack occurs when part of the heart dies as a result of lack of blood supply. The normal cause is a build up of plaque within the arteries known as atherosclerosis. Heart attacks can be caused by blood clots but these clots are more likely to form in places where the arteries have been damaged by atherosclerosis.
Risk factors for a heart attack
Coronary heart disease occurs as a result of an interaction between inheritance and the environment, which includes body fat, diet, smoking, alcohol and drug abuse and lack of regular exercise. Despite the fact that the traits are inherited it does not mean that the recommended treatment is the same, medication is still very much prescribed on an individual basis. However even with inherited traits a regression of the progress of the disease is possible and effective screening can be important if inherited traits come into the equation.
Smoking
The risk of arterial and heart disease increases with every cigarette smoked. Approximately forty percent of smokers die as a direct result of heart disease. Peripheral arterial disease can result in blood clots, infections and gangrene that can lead to amputations of the toes and fingers. Cigarettes contain nicotine and carbon monoxide; Nicotine makes the heart work harder to pump blood around the body, and carbon monoxide makes it beat faster. Cigarette smokers have on average a seventy percent higher chance of dying from coronary heart disease as non-smokers but the risk increases with the amount of cigarettes smoked.
Diabetes
Two out of three people who develop adult onset diabetes die either from a heart attack or a stroke.
High cholesterol level
The majority of diabetics also suffer from high cholesterol levels, ad both off these factors increase the risk of a stroke and heart disease. Improving your cholesterol level is as vital as improving your blood glucose levels.
High blood pressure
Blood pressure is the force the blood exerts on the arteries and if it is too high it can cause heart attacks and strokes. It is known as the silent killer because it often has no symptoms.
Family history of heart attack
· Genetics
Modern technological advances are making it possible to deal with a few of the genetic defects of the heart, but it still remains one of the factors outside of any ones control. Inheritance is still important in the development of coronary heart disease, as eighty percent of people with heart problems have a genetic lipoprotein abnormality.
Atherosclerosis (hardening of the arteries)
A plaque build-up of fatty deposits in the arteries causes them to harden and in effect constrain the passage of blood through them.
Lack of exercise
Everyone’s body benefits from a half an hour of aerobic activity about three or four times a week. That is exercise, which increases your heart rate slightly.
Obesity
Nowadays whether or not you fall into a safe band of weight control is by assessing your body weight in relation to your height. The categories are
Underweight = <18.5 weight =" between" overweight =" between" obesity =" ">30
How to assess your body mass index.
It is your weight in kilograms or pound divided by the square of your height in meters, or inches. There is an example below to calculate the body mass index in metric.
For instance, if your height is 1.86 meters, you multiply 1.86 by 1.86
1.86 x 1.86 = 3.4596.
Your weight is 74.8 kilos then your body mass is calculated by dividing your weight by your height squared.
74.8 (Your weight) / 3.4596 = 20.80In general the medical profession agree that between 19 and 22 is the healthiest wei8ght band and in this instance the weight falls within that band.
Male sex
Despite the fact that the statistics below make depressing reading the facts point to the fact that it is lack of care that causes these figures. Men who take care to keep themselves fit and keep their weight blood pressure and cholesterol levels under control are no more at risk than women. Most of the factors, which bring on premature coronary disease are within all our control.
· The average age for men to suffer their first heart attack is 66 years of age.[i]
· Half the men who have a heart attack before they are 65 will not have a mortality rate of longer than eight years [ii]
· Between 70 and 80 percent of immediate cardiac events with no warning occur to men.[iii]
Assessing Individual risk of a heart attack
The following information is a basic fact sheet you need to know to assess your risk of heart disease.
· Are you a smoker and if you are an ex smoker have you given up over two years ago.
· Your cholesterol levels of HDL AND LDL.
· Evidence of diabetes within the family
Your blood pressure
Your body mass index
Your inherited heart history and family history of heart disease.
Your risk is low risk if ALL the following are present
nonsmoker
total cholesterol <> 40 mg/dL
systolic blood <>[i] American Heart Association. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics—2005 Update. Dallas, Texas: American Heart Association, 2005.
[ii] Hurst W(2002.). The Heart, Arteries, and Veins. 10th ed. New York: McGraw Hill;
[iii] Hurst W(2002.). The Heart, Arteries, and Veins. 10th ed. New York: McGraw Hill;
ARTICLE 4
Angina and Chest Pains
In this Article
· What is Angina Pectoris?
· Types of Angina
· Treatment for Angina
· Instances when pains in the chest are not as a result of heart disease.
What is Angina Pectoris?
Angina pectoris is a symptom of a condition called myocardial ischemia, and it is a type of heart disease, which results in pains in the chest. The pains can spread to the neck back and upper arm regions. Myocardial is the adjective referring to the heart muscles, and ischemia is insufficient blood supply. Angina pectoris occurs when one of the blood vessels to the heart is blocked or has narrowed
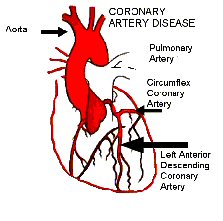
Angina is pains in the chest that result from a restricted blood supply to the heart. The pain occurs as pressure or squeezing but it can also feel like indigestion. Angina is always a symptom of coronary heart disease, resulting from a build up of plaque
Whilst it is possible to have angina when resting it is usually brought on by exertive exercise, which may be climbing stairs or power walking, whilst walking at an ordinary pace on the flat does not bring on an attack. An angina attack is always a warning that a heart attack may be imminent.
Types of Angina
There are three distinct types of angina and your treatment and prognosis depends on your understanding of the different types.
· Stable Angina
Stable angina has a pattern to it, it occurs when the heart is working under strain, either mental or physical. It is the most predictable and manageable of the anginas. The pain in general recedes a few minutes after you either take medicine normally nitro-glycerine or rest. Whilst it is not a heart attack it does increase your risk of having a heart attack in the future.
· Unstable angina
Unstable angina is the exact opposite of stable angina it always requires emergency treatment. Niether both rest nor angina treatment relieves it and it has no pattern. In fact a heart attack can occur at any point with unstable angina. It is nearly always caused by atherosclerosis, though the artery may be restricted by a blood clot. Infections and inflammation as well as secondary causes can lead to unstable angina.
· Prinzmetal's angina or variant angina
Is a form of unstable angina caused by a coronary artery spasm. It can be a painful condition, which is normally felt during nighttime sleeping hours whilst the patient is at rest it has no relationship to physical or mental exertion. Nearly seventy percent of sufferers’ have atherosclerosis in at least one of the major heart vessels and it is normal for the pain to be felt in the region of the blockage.
· Variant angina
This type of angina is rare, as less than two percent of angina sufferers’ have this type. With stable and unstable angina the patients who have it are normally elderly, but this type can affect the young. It manifests itself as chest pains late at night or in the early hours of the morning, it does respond to treatment.
Treatment for Angina
How Is Angina Treated?
Treatments for angina is designed to reduce the frequency and severity of the physical attacks, by doing this you reduce the risk of a heart attack. Stable angina may well be treated by lifestyle changes that are more heart friendly and medication.
Lifestyle changes
· Reduce physical exertions.
Angina can be aggravated by physical activity but by reducing hard physical exertions there is not the same strain on the heart. The first thing that you need to do is change your living habits to avoid bringing on an episode of angina
· Avoid rich meals
Many people who suffer from angina cannot tell whether their chest pains are a result of angina or of eating heavy rich meals. If you avoid over eating the ability to confuse the two symptoms is lessened.
· At all cost reduce stress levels
Stress reduction and management are part of all campaigns to reduce the severity and frequency of angina attacks. If there are times when stress levels cannot be avoided then it is imperative that you learn to handle that stress without straining your heart.
Diet
If you are overweight bring your weight down to a body mass index outside the range of obesity. At the same time reduce your cholesterol, avoid food which raise your blood pressure. Reduce your salt intake.
Stop smoking
Implement a level of gentle but regular physical exercise, walk for about twenty minutes three or four times a week.
Take medication as directed
Medications
Nitrates are the fastest acting medicines to treat angina as they dilate the blood vessels immediately, as they relax then the constriction caused by lack of blood is eased. The most common method id administration is by dissolving them under the tongue or a spray. They are taken long term to reduce angina as well as being administered during an angina attack.
Instances when pains in the chest are not as a result of heart disease.
· Indigestion
· Heart burn
· Lung infections or lung inflammations.
ARTICLE 5
ATHEROSCLEROSIS
In This Article
· What is atherosclerosis
· Warning signs
· Risk Factors
· Cholesterol and diet.
· Treatment
What is atherosclerosis
The word is derived from Greek, the word for gruel is athero and the word for hardness is sclerosis. As we age we are all subject to the process of atherosclerosis when fatty substances, such as cholesterol, calcium, and cellular waste products build up within our medium and large arteries. This destructive fatty substance is called plaque. As the plaque grows it restricts the blood passing smoothly through the arteries. They may remain in place where they form or they can rupture and travel to other parts of the artery where they cause blood clots to form.
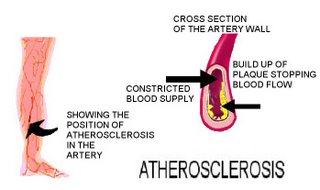
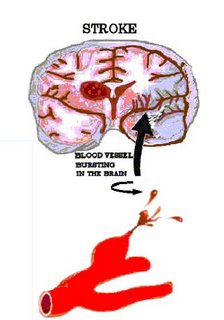
Long-term effects occur when they constrain the blood flow, if it blocks the vessels to the heart then the result is a heart attack. If is occurs in the leg muscles then it causes walling difficulties and can result in gangrene. When it restricts the blood to the brain it is a stroke.
Atherosclerosis also leads to hypertension because the blood being forced through ever narrowing articles exerts greater pressure on the narrowing walls of the arteries. In turn this increases the risk of strokes and heart attacks.
Atherosclerosis is a complex condition, which can start in childhood, and its cause is not completely clear. Some specialists think that there is a connection between atherosclerosis and the endothelium, which is the interface that separates the artery from the arterial blood. As a condition it has no symptoms until it has advanced to the point that it causes chest pain.
WARNING SIGNS
When arteries to the brain are affected.
· Headaches
· Dizzy spells
· Ringing of ear
· Memory problems
· Poor concentration
· Mood changes
When arteries to the heart are affected
· Chest pain (angina pectoris)
· Elevated blood pressure
When arteries to the arms or legs are affected.
· Aching muscles
· Fatigue
· Cramping pains in the calves
· Pain in the hips and thighs may occur depending on the affected arteries
Risk Factors
Congenital
· Premature Cardiovascular Disease
Anyone with congenital premature cardiovascular disease, in his or her family history is at risk. This element of risk cannot be controlled because it is genetic, but there are other risks than can be altered.
Controllable risks
· Elevated levels of cholesterol and triglyceride in the blood
A high level of bad cholesterol in the form of LDL is at risk and a high reading is over 100 mg/dL
· High blood pressure.
· Smoking
· Diabetes Mellitus
· Obesity
· Insufficient physical activity
CHOLESTEROL AND DIET
Cholesterol is produced by the liver and ingested in certain animal food types. The livers of animal also produce cholesterol so any product from the liver has the animal’s cholesterol in it and this is transferred to humans on consumption, therefore any liver products are high in cholesterol. Other foods with high level are prawns, egg yolks, meat, seafood and whole milk dairy products such as cheese butter and yogurt. Consequently if your levels of cholesterol are high the American Heart Association recommends less than
150 grams a day of animal protein. Plant proteins such as grains and pulses can safely supplement protein levels, as they contain no cholesterol, there is no cholesterol at all in any plant product. Reducing your intake of dairy products and using lower fat dairy products such as skimmed milk helps reduce your cholesterol.
TREATMENT
The prevention of Atherosclerosis is a life-long process, with each individual assessing his or her own personal risk factors. Agents, which lower the lipid levels of the blood stream, can control plaque and other drugs can help to halt the progression of the disease.
ARTICLE 6
Cardiac Cycle
In this Article
· Cardiac Definition and activity
· The cardiac cycle
· Regulation of the Cardiac Cycle
Cardiac Definition and activity
Cardiac is an adjective, which refers to the heart, cardiac cycle therefore is the cycle of heart activity, and the derivative of the word is the Greek kardia καρδια meaning heart.
The heart is a hollow muscular organ that acts as a pump, and the events of the cardiac cycle are divided into four phases. The first two are the diastole or the relaxation phase, whilst the heart is empty and relaxed prior to filling with blood, and the time that the ventricles actually fill with blood. The diastole phases last slightly longer than the systole phase when the pressure builds in the ventricles and the heart contracts ready to eject the oxygenated blood from the heart ventricles to the body. The final period of the cardiac cycle is when tall the ventricles are repolarizing and all three valves are closed.
The cardiac cycle
Whilst the heart is in its early diastolic phase, the ventricles and the atria which is the hearts upper two chambers are relaxed, whilst the blood flows into the left and right atria.
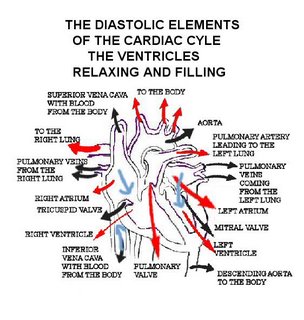
As the blood collects in the upper chambers of the heart, the S A node, which acts as the heart’s natural pacemaker transmits an electrical signal which forces the atria to contract. The right atrium receives the blood from both the superior vena cava, and the inferior cava, and through the coronary sinus, which is receiving blood from the heart muscle.
The right atrium transfers the blood through the right atrioventicular valve, also known as the as the tricuspid valve, into the right ventricle of the heart. The function of the tricuspid valve is protective it ensures the blood flows only from the right atria to the right ventricle, and none of it accidentally flows back.
Whilst the atria are contracting, the pressure increases in the upper chambers, concentrating toward the open atrioventicular valves; they ensure the swift passage of blood into the ventricles. Once all the blood from that single heartbeat has left the atria, then the ventricular chambers close, which prevents any blood reversing its direction.
The second phase of the action is pumping the blood is the systolic phase, which is specifically when the left ventricle is contracting.
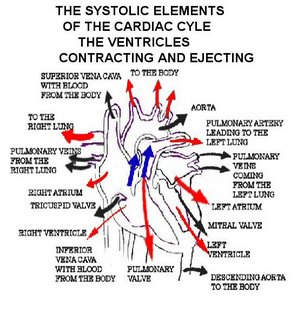
The ventricles contract when the S A node travels to the ventricles. The tricuspid and mitral valves both close to prevent the blood flowing back to the ventricles. In turn this causes pressure that force the pulmonary and the aortic valves open creating a passage for the blood to the lungs. At this point in the cardiac cycle the blood is not being ejected from the ventricles, the pressure is building to prepare for the ejection of the deoxygenated blood to the lung to collect oxygen. The pressure in the ventricle must exceed the pressure in the Aorta for blood to be ejected from the heart. The blood exits the lungs rich in oxygen, and flows from the left ventricle to the other parts of the body to distribute the oxygen needed fro the tissues to function.
Once the blood moves into the pulmonary artery and the aorta, the ventricles relax and the pulmonary and aortic valves close. Once the pressure in the ventricles reduces, the tricuspid and mistral valves open to repeat the cycle.
Regulation of the Cardiac Cycle
Cardiac muscle is unique as it is myogenic, or capable of contracting and relaxing on its own. All the other bodies’ skeletal muscles need conscious or a reflexive stimulation to function. However the cardiac contractions can be altered as a result of a perception of danger and exercise. Each cardiac cycle takes approximately 0.8 second and spans the time from the end of one heart contraction to the end of the subsequent contraction, and in general the heart contract about 72 times a minute. Even when the heart is surgically removed from the body it is capable of beating for several hours providing it has the correct salts and nutrients.
ARTICLE 1
Heart Attack
In This Article
· Common Names For a heart attack
· What is A heart Attack
· Warning signs of A heart attack
· Who is at risk from a heart attack
Common Names For a heart attack
A heart attack goes under many names including the following: -
· Myocardial infarction or MI,
· Acute myocardial infarction or AMI
· Acute coronary syndrome
· Coronary thrombosis
· Coronary occlusion
What is A heart Attack
A myocardial infarction occurs when an area of the heart’s muscle dies or is permanently damaged because of inadequate supply of oxygen, which results from a blockage.
The blockage is usually caused in the coronary artery as the blockage results in a arrhythmia, which is an irregular heart rhythm. This irregular heartbeat may prevent the pumping function of the heart and as this is the primary heart function it can lead to death. If death does not occur immediately the blockage must be treated with a few hours or the area of the heart muscle, which has been affected by the arrhythmia, will die and be replaced by scar tissue.
A clot in the coronary artery interrupts the flow of blood and oxygen to the heart muscle, leading to the death of heart cells in the immediate vicinity. The damaged heart muscle loses its ability to contract, and the remaining heart muscle needs to compensate for that weakened area. The larger the area of the heart that is damaged means that the remaining “healthy” area cannot cope. This is critical because of the blood supply ceases for more than a few minutes permanent damage is caused in the muscle cells, which results in death or permanent disablement. Statistically a million people in the U.S. suffer a heart attack annually and fifty percent die, of these deaths just over a half will die in the first hour following the heart attack.
The brutal truth of a heart attack is that emergency treatment must be sought IMMEDIATELY you suspect that a heart attack is occurring. Emergency procedures can be implemented to restore the flow of blood to the blocked artery, and this can prevent permanent damage to the heart. Statistically most people do not seek treatment until over two hours after the start of symptoms, and many leave it for over twelve hours. Prompt action saves lives in this situation, as the delay is unsustainable in many cases.

The clot has usually formed in the coronary artery as a r4esult of narrowing due to atherosclerosis. The atherosclerotic plaque inside the arterial wall sometimes cracks or splinters, which trigger the formation of a clot, which may be called a thrombus, leading to the adjective thrombosis.
Warning signs of A heart attack
The warning signs are approximate because the symptoms of a heart attack are too diverse to be simplified. As can be seen these signs are very easily confused with non life threatening inconsequential conditions such as eating too much! However the damage and death resulting from a heart attack are serious enough not to be trivialized or ignored, and the survivor’s of a heart attack are those that took the decision to be safe not sorry. The sooner treatment is administered the safer a patient will be.
Who Is at Risk From A Heart Attack?
There is no such thing as a typical profile for a heart attack victim, but it is certain that it is the number one killer in the most of the first world today. There are some risk factors that are irrefutable –
· Advancing age
Over 80 percent of people who die of coronary heart disease are 65 years of age or older.
Beyond this age women are more likely to die than men when they have a heart attack, although it may not be immediate it may be within a few weeks.
· Gender
After menopause women have a higher risk than men of not surviving a heart attack, but men have heart attacks earlier and more often.
· Heredity Factors
Statistically Africans have a higher rate of blood pressure than Caucasians and their risk of having a heart attack is proportionally higher. Some Asian groups have higher risk Gujarati’s tend to have a higher number of heart attacks, as do Mexicans and Polynesians. However the factors are not necessarily genetic they may be as a result of higher obesity rate coupled with higher levels of the onset of middle age diabetes.
In comclusion, there are some riskl factors that there is little you can do about, but that fact alone makes it more crucial that the things you can do such as keeping your weight within a safe band, have regular exercise and look at your levels of cholesterol and blood pressure.
ARTICLE 2
Heart Attack Symptoms
In This Article
· Variations in Symptoms.
· Coronary Heart Disease
· General Indicators Of a Heart Attack
· Angina as a precursor of a heart attack.
· Silent Heart Attacks
Variations in Symptoms.
The bad news for a assessing whether or not you are suffering from a heart attack is that no single heart attack resembles any other, and even if you have had one before there is no guarantee that the symptoms will be the same. The symptoms of a heart attack depends on the severity of a heart attack and how much damage is caused to the heart cells, whether they actually die or are damaged. To further complicate matter there are silent heart attacks that occur without any symptoms.
General Indicators Of a Heart Attack
· Chest discomfort.
The majority of heart attacks involve discomfort in the chest that either lasts for more than a few minutes, or goes away and returns. This discomfort can take many forms it is not always pain, it may be pressure a feeling of fullness, contracting or squeezing of the chest. Also it may be confused with minor ailments such as heartburn or indigestion because it may indeed manifest the first symptoms.
· Discomfort in other areas of the upper body.
There may be pain, discomfort, or a sense of numbness in one or both of the arms, the back, neck, jaw, or the stomach.
· Shortness of breath.
May or may not accompany a heart attack, it may come before during or after the heart attack itself.
· Other symptoms.
These may be cold sweats, leaving a film of sweat on the skin or a feeling of clamminess. The patient may feel light headed or dizzy, as if they have sat up too quickly, or they may feel nausea and want to vomit.
· Gender symptoms
Women statistically have a greater risk of experiencing pain between the shoulders and this tends to make then defer diagnosis and therefore treatment.
· Coronary Heart Disease or angina.
The heart like any other of the human body organs needs sufficient oxygen to function, and if deprived of this it will react and cause pain. The correct name for this condition is
Myocardial ischemia.

· Angina as A Precursor of a Heart Attack.
Typically the heart tends to beat faster after a big meal, during and after hard physical exertion, in the cold, or during periods of stress or emotional discomfort. If the arteries cannot supply enough oxygen in these charged times then the heart suffers from oxygen deficiency and it reacts by creating pain known as angina pectoris.

Whilst it is difficult to tell if a pain is indeed a heart attack pain, the pain resulting from angina pectoris tends to be distinct and is often described as a strangulating pain or a feeling of suffocation. It tends to be more severe and intense than heartburn or indigestion In may cases it appears to start under the breastbone and radiates on the left side to the throat, neck, shoulder and maybe as far down as the arm, it can in rarer cases emanate on the right side as well.
As a result of its intensity the first angina attack can be frightening, but despite the severity of the pain, they generally subside after about fifteen twenty minutes. In the event of them lasting longer a medical check up should be sought immediately. If angina carries on for a long time it may well lead to a full blown heart attack.
· Silent Heart Attacks
These can occur with no symptoms and therefore no treatment will be sought, but statistically they are more likely to happen to women, diabetics and those over 65.
ARTICLE 3
How TO Prevent Heart Attacks.
In this Article
· Heart Attack
· Risk factors for a heart attack
· Assessing Individual risk of a heart attack
Heart Attack
A heart attack occurs when part of the heart dies as a result of lack of blood supply. The normal cause is a build up of plaque within the arteries known as atherosclerosis. Heart attacks can be caused by blood clots but these clots are more likely to form in places where the arteries have been damaged by atherosclerosis.
Risk factors for a heart attack
Coronary heart disease occurs as a result of an interaction between inheritance and the environment, which includes body fat, diet, smoking, alcohol and drug abuse and lack of regular exercise. Despite the fact that the traits are inherited it does not mean that the recommended treatment is the same, medication is still very much prescribed on an individual basis. However even with inherited traits a regression of the progress of the disease is possible and effective screening can be important if inherited traits come into the equation.
Smoking
The risk of arterial and heart disease increases with every cigarette smoked. Approximately forty percent of smokers die as a direct result of heart disease. Peripheral arterial disease can result in blood clots, infections and gangrene that can lead to amputations of the toes and fingers. Cigarettes contain nicotine and carbon monoxide; Nicotine makes the heart work harder to pump blood around the body, and carbon monoxide makes it beat faster. Cigarette smokers have on average a seventy percent higher chance of dying from coronary heart disease as non-smokers but the risk increases with the amount of cigarettes smoked.
Diabetes
Two out of three people who develop adult onset diabetes die either from a heart attack or a stroke.
High cholesterol level
The majority of diabetics also suffer from high cholesterol levels, ad both off these factors increase the risk of a stroke and heart disease. Improving your cholesterol level is as vital as improving your blood glucose levels.
High blood pressure
Blood pressure is the force the blood exerts on the arteries and if it is too high it can cause heart attacks and strokes. It is known as the silent killer because it often has no symptoms.
Family history of heart attack
· Genetics
Modern technological advances are making it possible to deal with a few of the genetic defects of the heart, but it still remains one of the factors outside of any ones control. Inheritance is still important in the development of coronary heart disease, as eighty percent of people with heart problems have a genetic lipoprotein abnormality.
Atherosclerosis (hardening of the arteries)
A plaque build-up of fatty deposits in the arteries causes them to harden and in effect constrain the passage of blood through them.
Lack of exercise
Everyone’s body benefits from a half an hour of aerobic activity about three or four times a week. That is exercise, which increases your heart rate slightly.
Obesity
Nowadays whether or not you fall into a safe band of weight control is by assessing your body weight in relation to your height. The categories are
Underweight = <18.5 weight =" between" overweight =" between" obesity =" ">30
How to assess your body mass index.
It is your weight in kilograms or pound divided by the square of your height in meters, or inches. There is an example below to calculate the body mass index in metric.
For instance, if your height is 1.86 meters, you multiply 1.86 by 1.86
1.86 x 1.86 = 3.4596.
Your weight is 74.8 kilos then your body mass is calculated by dividing your weight by your height squared.
74.8 (Your weight) / 3.4596 = 20.80In general the medical profession agree that between 19 and 22 is the healthiest wei8ght band and in this instance the weight falls within that band.
Male sex
Despite the fact that the statistics below make depressing reading the facts point to the fact that it is lack of care that causes these figures. Men who take care to keep themselves fit and keep their weight blood pressure and cholesterol levels under control are no more at risk than women. Most of the factors, which bring on premature coronary disease are within all our control.
· The average age for men to suffer their first heart attack is 66 years of age.[i]
· Half the men who have a heart attack before they are 65 will not have a mortality rate of longer than eight years [ii]
· Between 70 and 80 percent of immediate cardiac events with no warning occur to men.[iii]
Assessing Individual risk of a heart attack
The following information is a basic fact sheet you need to know to assess your risk of heart disease.
· Are you a smoker and if you are an ex smoker have you given up over two years ago.
· Your cholesterol levels of HDL AND LDL.
· Evidence of diabetes within the family
Your blood pressure
Your body mass index
Your inherited heart history and family history of heart disease.
Your risk is low risk if ALL the following are present
nonsmoker
total cholesterol <> 40 mg/dL
systolic blood <>[i] American Heart Association. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics—2005 Update. Dallas, Texas: American Heart Association, 2005.
[ii] Hurst W(2002.). The Heart, Arteries, and Veins. 10th ed. New York: McGraw Hill;
[iii] Hurst W(2002.). The Heart, Arteries, and Veins. 10th ed. New York: McGraw Hill;
ARTICLE 4
Angina and Chest Pains
In this Article
· What is Angina Pectoris?
· Types of Angina
· Treatment for Angina
· Instances when pains in the chest are not as a result of heart disease.
What is Angina Pectoris?
Angina pectoris is a symptom of a condition called myocardial ischemia, and it is a type of heart disease, which results in pains in the chest. The pains can spread to the neck back and upper arm regions. Myocardial is the adjective referring to the heart muscles, and ischemia is insufficient blood supply. Angina pectoris occurs when one of the blood vessels to the heart is blocked or has narrowed

Angina is pains in the chest that result from a restricted blood supply to the heart. The pain occurs as pressure or squeezing but it can also feel like indigestion. Angina is always a symptom of coronary heart disease, resulting from a build up of plaque
Whilst it is possible to have angina when resting it is usually brought on by exertive exercise, which may be climbing stairs or power walking, whilst walking at an ordinary pace on the flat does not bring on an attack. An angina attack is always a warning that a heart attack may be imminent.
Types of Angina
There are three distinct types of angina and your treatment and prognosis depends on your understanding of the different types.
· Stable Angina
Stable angina has a pattern to it, it occurs when the heart is working under strain, either mental or physical. It is the most predictable and manageable of the anginas. The pain in general recedes a few minutes after you either take medicine normally nitro-glycerine or rest. Whilst it is not a heart attack it does increase your risk of having a heart attack in the future.
· Unstable angina
Unstable angina is the exact opposite of stable angina it always requires emergency treatment. Niether both rest nor angina treatment relieves it and it has no pattern. In fact a heart attack can occur at any point with unstable angina. It is nearly always caused by atherosclerosis, though the artery may be restricted by a blood clot. Infections and inflammation as well as secondary causes can lead to unstable angina.
· Prinzmetal's angina or variant angina
Is a form of unstable angina caused by a coronary artery spasm. It can be a painful condition, which is normally felt during nighttime sleeping hours whilst the patient is at rest it has no relationship to physical or mental exertion. Nearly seventy percent of sufferers’ have atherosclerosis in at least one of the major heart vessels and it is normal for the pain to be felt in the region of the blockage.
· Variant angina
This type of angina is rare, as less than two percent of angina sufferers’ have this type. With stable and unstable angina the patients who have it are normally elderly, but this type can affect the young. It manifests itself as chest pains late at night or in the early hours of the morning, it does respond to treatment.
Treatment for Angina
How Is Angina Treated?
Treatments for angina is designed to reduce the frequency and severity of the physical attacks, by doing this you reduce the risk of a heart attack. Stable angina may well be treated by lifestyle changes that are more heart friendly and medication.
Lifestyle changes
· Reduce physical exertions.
Angina can be aggravated by physical activity but by reducing hard physical exertions there is not the same strain on the heart. The first thing that you need to do is change your living habits to avoid bringing on an episode of angina
· Avoid rich meals
Many people who suffer from angina cannot tell whether their chest pains are a result of angina or of eating heavy rich meals. If you avoid over eating the ability to confuse the two symptoms is lessened.
· At all cost reduce stress levels
Stress reduction and management are part of all campaigns to reduce the severity and frequency of angina attacks. If there are times when stress levels cannot be avoided then it is imperative that you learn to handle that stress without straining your heart.
Diet
If you are overweight bring your weight down to a body mass index outside the range of obesity. At the same time reduce your cholesterol, avoid food which raise your blood pressure. Reduce your salt intake.
Stop smoking
Implement a level of gentle but regular physical exercise, walk for about twenty minutes three or four times a week.
Take medication as directed
Medications
Nitrates are the fastest acting medicines to treat angina as they dilate the blood vessels immediately, as they relax then the constriction caused by lack of blood is eased. The most common method id administration is by dissolving them under the tongue or a spray. They are taken long term to reduce angina as well as being administered during an angina attack.
Instances when pains in the chest are not as a result of heart disease.
· Indigestion
· Heart burn
· Lung infections or lung inflammations.
ARTICLE 5
ATHEROSCLEROSIS
In This Article
· What is atherosclerosis
· Warning signs
· Risk Factors
· Cholesterol and diet.
· Treatment
What is atherosclerosis
The word is derived from Greek, the word for gruel is athero and the word for hardness is sclerosis. As we age we are all subject to the process of atherosclerosis when fatty substances, such as cholesterol, calcium, and cellular waste products build up within our medium and large arteries. This destructive fatty substance is called plaque. As the plaque grows it restricts the blood passing smoothly through the arteries. They may remain in place where they form or they can rupture and travel to other parts of the artery where they cause blood clots to form.

Long-term effects occur when they constrain the blood flow, if it blocks the vessels to the heart then the result is a heart attack. If is occurs in the leg muscles then it causes walling difficulties and can result in gangrene. When it restricts the blood to the brain it is a stroke.
Atherosclerosis also leads to hypertension because the blood being forced through ever narrowing articles exerts greater pressure on the narrowing walls of the arteries. In turn this increases the risk of strokes and heart attacks.
Atherosclerosis is a complex condition, which can start in childhood, and its cause is not completely clear. Some specialists think that there is a connection between atherosclerosis and the endothelium, which is the interface that separates the artery from the arterial blood. As a condition it has no symptoms until it has advanced to the point that it causes chest pain.
WARNING SIGNS
When arteries to the brain are affected.
· Headaches
· Dizzy spells
· Ringing of ear
· Memory problems
· Poor concentration
· Mood changes
When arteries to the heart are affected
· Chest pain (angina pectoris)
· Elevated blood pressure
When arteries to the arms or legs are affected.
· Aching muscles
· Fatigue
· Cramping pains in the calves
· Pain in the hips and thighs may occur depending on the affected arteries
Risk Factors
Congenital
· Premature Cardiovascular Disease
Anyone with congenital premature cardiovascular disease, in his or her family history is at risk. This element of risk cannot be controlled because it is genetic, but there are other risks than can be altered.
Controllable risks
· Elevated levels of cholesterol and triglyceride in the blood
A high level of bad cholesterol in the form of LDL is at risk and a high reading is over 100 mg/dL
· High blood pressure.
· Smoking
· Diabetes Mellitus
· Obesity
· Insufficient physical activity
CHOLESTEROL AND DIET
Cholesterol is produced by the liver and ingested in certain animal food types. The livers of animal also produce cholesterol so any product from the liver has the animal’s cholesterol in it and this is transferred to humans on consumption, therefore any liver products are high in cholesterol. Other foods with high level are prawns, egg yolks, meat, seafood and whole milk dairy products such as cheese butter and yogurt. Consequently if your levels of cholesterol are high the American Heart Association recommends less than
150 grams a day of animal protein. Plant proteins such as grains and pulses can safely supplement protein levels, as they contain no cholesterol, there is no cholesterol at all in any plant product. Reducing your intake of dairy products and using lower fat dairy products such as skimmed milk helps reduce your cholesterol.
TREATMENT
The prevention of Atherosclerosis is a life-long process, with each individual assessing his or her own personal risk factors. Agents, which lower the lipid levels of the blood stream, can control plaque and other drugs can help to halt the progression of the disease.
ARTICLE 6
Cardiac Cycle
In this Article
· Cardiac Definition and activity
· The cardiac cycle
· Regulation of the Cardiac Cycle
Cardiac Definition and activity
Cardiac is an adjective, which refers to the heart, cardiac cycle therefore is the cycle of heart activity, and the derivative of the word is the Greek kardia καρδια meaning heart.
The heart is a hollow muscular organ that acts as a pump, and the events of the cardiac cycle are divided into four phases. The first two are the diastole or the relaxation phase, whilst the heart is empty and relaxed prior to filling with blood, and the time that the ventricles actually fill with blood. The diastole phases last slightly longer than the systole phase when the pressure builds in the ventricles and the heart contracts ready to eject the oxygenated blood from the heart ventricles to the body. The final period of the cardiac cycle is when tall the ventricles are repolarizing and all three valves are closed.
The cardiac cycle
Whilst the heart is in its early diastolic phase, the ventricles and the atria which is the hearts upper two chambers are relaxed, whilst the blood flows into the left and right atria.

As the blood collects in the upper chambers of the heart, the S A node, which acts as the heart’s natural pacemaker transmits an electrical signal which forces the atria to contract. The right atrium receives the blood from both the superior vena cava, and the inferior cava, and through the coronary sinus, which is receiving blood from the heart muscle.
The right atrium transfers the blood through the right atrioventicular valve, also known as the as the tricuspid valve, into the right ventricle of the heart. The function of the tricuspid valve is protective it ensures the blood flows only from the right atria to the right ventricle, and none of it accidentally flows back.
Whilst the atria are contracting, the pressure increases in the upper chambers, concentrating toward the open atrioventicular valves; they ensure the swift passage of blood into the ventricles. Once all the blood from that single heartbeat has left the atria, then the ventricular chambers close, which prevents any blood reversing its direction.
The second phase of the action is pumping the blood is the systolic phase, which is specifically when the left ventricle is contracting.

The ventricles contract when the S A node travels to the ventricles. The tricuspid and mitral valves both close to prevent the blood flowing back to the ventricles. In turn this causes pressure that force the pulmonary and the aortic valves open creating a passage for the blood to the lungs. At this point in the cardiac cycle the blood is not being ejected from the ventricles, the pressure is building to prepare for the ejection of the deoxygenated blood to the lung to collect oxygen. The pressure in the ventricle must exceed the pressure in the Aorta for blood to be ejected from the heart. The blood exits the lungs rich in oxygen, and flows from the left ventricle to the other parts of the body to distribute the oxygen needed fro the tissues to function.
Once the blood moves into the pulmonary artery and the aorta, the ventricles relax and the pulmonary and aortic valves close. Once the pressure in the ventricles reduces, the tricuspid and mistral valves open to repeat the cycle.
Regulation of the Cardiac Cycle
Cardiac muscle is unique as it is myogenic, or capable of contracting and relaxing on its own. All the other bodies’ skeletal muscles need conscious or a reflexive stimulation to function. However the cardiac contractions can be altered as a result of a perception of danger and exercise. Each cardiac cycle takes approximately 0.8 second and spans the time from the end of one heart contraction to the end of the subsequent contraction, and in general the heart contract about 72 times a minute. Even when the heart is surgically removed from the body it is capable of beating for several hours providing it has the correct salts and nutrients.